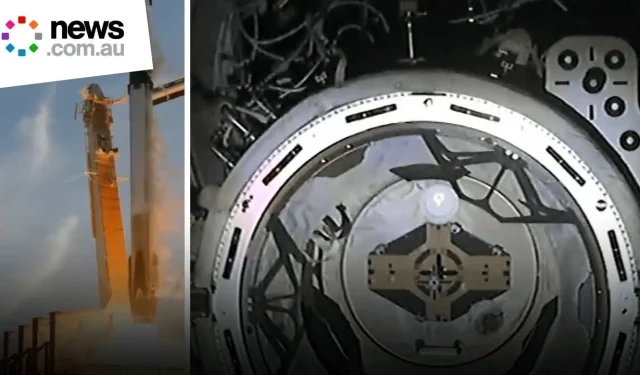
SpaceX’s Rescuing Endeavor: A Milestone in Human Spaceflight
In a historic move, SpaceX’s spacecraft has successfully docked at the International Space Station (ISS) as part of a daring mission to rescue stranded astronauts. This unprecedented operation underscores the growing capabilities of private space exploration companies in supporting government space missions.
The Rescue Context
This mission comes in response to an urgent situation involving astronauts who have been rendered stranded due to unforeseen technical issues on previous missions. The docking was executed flawlessly, ensuring the safe passage of astronauts back to Earth, while also emphasizing the importance of collaboration between private aerospace companies like SpaceX and international space agencies.
Technical Details of the Docking Process
The docking procedure involved advanced maneuvers and precise calculations executed by both onboard and ground control teams. The SpaceX capsule approached the ISS at a calculated speed, employing a series of automated systems designed to facilitate soft docking—a critical component for ensuring the safety of crews during such operations.
Broader Implications for Space Exploration
This significant feat not only demonstrates SpaceX’s technological advancements but also has broader implications for the future of human spaceflight. As private companies increasingly participate in space exploration, they are redefining traditional roles that have historically been dominated by governmental agencies. The efficiency and effectiveness shown in this mission may lead to enhanced partnerships between private enterprises and national space agencies.
Potential Consequences and Future Directions
The success of this rescue mission bolsters public confidence in private space ventures, which may attract more investments and interest in upcoming projects. Furthermore, it raises discussions regarding the establishment of protocols for future rescue missions and the overall safety of astronauts in space. This incident could serve as a model for how future emergencies are managed, potentially shaping policy and operational standards in the sound management and evacuation of crewed space missions.